Elasmobranchii (sharks and rays) >
Carcharhiniformes (Ground sharks) >
Triakidae (Houndsharks) > Galeorhininae
Etymology: Galeorhinus: galeo, probably based on G. galeus (see below); rhinus, an ancient name for sharks, from rhine (Gr.), rasp, alluding to their rasp-like skin (See ETYFish); galeus: From galeos, a small shark or dogfish per Aristotle (sometimes translated as weasel), possibly referring to the pointed snouts, swift movements and/or rapacious feeding behavior of smaller predatory sharks1 (See ETYFish).
More on author: Linnaeus.
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
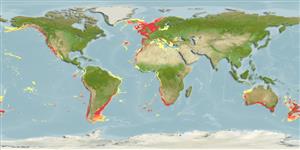
Marine; benthopelagic; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 0 - 1100 m (Ref. 26346), usually 2 - 471 m (Ref. 43939). Subtropical; 70°N - 58°S, 111°E - 37°E
World-wide in temperate waters (Ref. 58085). Western Atlantic: southern Brazil to Argentina. Eastern Atlantic: Iceland, Norway, Faeroe Islands, British Isles to the Mediterranean and Senegal; Namibia to South Africa (Western Indian Ocean). Western Pacific: Australia and New Zealand. Eastern Pacific: British Columbia (Canada) to southern Baja California, Gulf of California; Peru and Chile. Questionable records in Ivory Coast, Nigerai, Gabon to Congo Dem Rep and Laysan Is. (Hawaii) (Ref 244).
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm 144.1, range 120 - 185 cm
Max length : 193 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 40637); 195.0 cm TL (female); common length : 160 cm TL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9258); max. published weight: 44.7 kg (Ref. 40637); max. reported age: 55 years (Ref. 6871)
Dorsal spines (total): 0; Anal spines: 0. A large houndshark with a long, pointed snout, a large mouth, and small blade-like teeth; 2nd dorsal about as large as anal fin and terminal caudal lobe as long as rest of fin (Ref. 5578). Greyish above, white below; young with black markings on fins (Ref. 5578).
Mainly demersal on continental and insular shelves, but also on the upper slopes, at depths from near shore to 550 m (Ref. 6871), but has been shown to be pelagic in the open ocean (frequently caught on floating tuna longlines over deep water, and many New Zealand-tagged specimens have been recaptured in Australia) (Ref. 26346). Occurs in small schools that are highly migratory in higher latitudes in their range (Ref. 244). There is pronounced partial segregation by size and sex in some areas (Ref. 244). Feeds on fishes (bottom as well as pelagic species, Ref. 26346), crustaceans, cephalopods, worms, and echinoderms (Ref. 244). Ovoviviparous (Ref. 50449). Targeted for human consumption, liver for squalene oil, fins for soup (Ref. 244); also utilized as fishmeal (Ref. 13563). Marketed fresh, dried-salted, and frozen (Ref. 9987). Adapts well in captivity if carefully captured and handled (Ref. 12951).
Ovoviviparous, without a yolk-sac placenta (Ref. 244). Embryos feed solely on yolk (Ref. 50449). 6 to 52 young in a litter (Ref. 26346). Litter size increases with the size of the mother. Embryos reach 30-36 cm TL at birth (Ref. 6080). In the southern waters of Australia, newly born and older juveniles (30-70 cm long) aggregate in 'nursery areas' found in shallow waters.They move to deeper coastal waters to over-winter. The following spring finds most of these young returning to their nursery areas. The older ones, aged 2 years and over move instead to eastern Bass Strait where most of the immature stock are found. The length of an average full-term embryo is 32 cm. Spawning frequency is once every year, ovulation occurring in early summer and parturition is completed by January of the following year. Gestation period lasts for about 12 months (Ref. 6390, 6871).
Compagno, L.J.V., 1984. FAO Species Catalogue. Vol. 4. Sharks of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date. Part 2 - Carcharhiniformes. FAO Fish. Synop. 125(4/2):251-655. Rome: FAO. (Ref. 244)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Human uses
Fisheries: highly commercial; gamefish: yes; aquarium: public aquariums
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 6.7 - 23.2, mean 12.3 °C (based on 7314 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 1.0000 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.00479 (0.00362 - 0.00632), b=2.99 (2.91 - 3.07), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this species (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 4.3 ±0.1 se; based on diet studies.
Generation time: 11.9 (6.9 - 14.7) years. Estimated as median ln(3)/K based on 12
growth studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Low, minimum population doubling time 4.5 - 14 years (rm=0.033; tmax=55; Fec=6-52).
Prior r = 0.06, 95% CL = 0.04 - 0.09, Based on 2 full stock assessments.
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Very high vulnerability (76 of 100).
Climate Vulnerability (Ref.
125649): High vulnerability (62 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 8.56 [1.46, 48.15] mg/100g; Iron = 0.465 [0.128, 1.502] mg/100g; Protein = 20 [18, 22] %; Omega3 = 0.18 [0.11, 0.30] g/100g; Selenium = 44.2 [13.5, 139.5] μg/100g; VitaminA = 13.1 [4.2, 44.7] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.409 [0.194, 0.769] mg/100g (wet weight); based on
nutrient studies.