Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range
Ecology
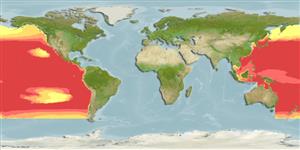
Marine; brackish; pelagic-oceanic; oceanodromous (Ref. 51243); depth range 1 - 550 m (Ref. 58302). Subtropical; 61°N - 52°S, 99°E - 70°W
North Pacific: Gulf of Alaska to southern California and Baja California and from Sakhalin Island in the southern Sea of Okhotsk south to northern Philippines. There are four substantiated records of this subspecies in the southern hemisphere: off Western Australia, southeast Pacific (37°11'S, 114°41'W) and Gulf of Papua (Ref. 10997). The species occurs mainly in the northern Pacific but ventures into New Zealand waters for at least three months during spring and early summer (Ref. 83312).
Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm
Max length : 300 cm FL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9340); common length : 200 cm FL male/unsexed; (Ref. 9340); max. published weight: 450.0 kg (Ref. 47525); max. reported age: 15 years (Ref. 83312)
Mean number of gill rakers 35.9. First ventrally directed parapophysis on vertebra number 8. Dorsal wall of body cavity has a narrow bulge with lateral concavity and wide lateral trough. Caudal keels dark.
Epipelagic, usually oceanic, but seasonally coming close to shore (Ref. 168). Tolerates ample temperature intervals (Ref. 168). Forms schools by size, sometimes with other scombrids (Ref. 168). Migrates between June and September in a northward direction along the coast of Baja California, Mexico and California (Ref. 168). A voracious predator that feeds on a wide variety of small schooling fishes and squids, also on crabs crabs and to a lesser degree on sessile organisms (Ref. 168). Marketed fresh and frozen.
Collette, B.B., 1995. Scombridae. Atunes, bacoretas, bonitos, caballas, estorninos, melva, etc. p. 1521-1543. In W. Fischer, F. Krupp, W. Schneider, C. Sommer, K.E. Carpenter and V. Niem (eds.) Guia FAO para Identification de Especies para lo Fines de la Pesca. Pacifico Centro-Oriental. 3 Vols. FAO, Rome. (Ref. 9340)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435: Version 2024-2)
Threat to humans
Harmless
Human uses
Fisheries: highly commercial; aquaculture: commercial; gamefish: yes
Tools
Special reports
Download XML
Internet sources
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature (Ref.
123201): 13.9 - 28.1, mean 24.3 °C (based on 983 cells).
Phylogenetic diversity index (Ref.
82804): PD
50 = 0.5039 [Uniqueness, from 0.5 = low to 2.0 = high].
Bayesian length-weight: a=0.01380 (0.00641 - 0.02973), b=3.03 (2.86 - 3.20), in cm total length, based on LWR estimates for this Genus-body shape (Ref.
93245).
Trophic level (Ref.
69278): 4.5 ±0.3 se; based on size and trophs of closest relatives
Generation time: 10.6 ( na - na) years. Estimated as median ln(3)/K based on 2
growth studies.
Resilience (Ref.
120179): Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (tm=3-5; tmax=15; K=0.1-0.2).
Prior r = 0.25, 95% CL = 0.17 - 0.38, Based on 3 full stock assessments.
Fishing Vulnerability (Ref.
59153): Very high vulnerability (76 of 100).
Climate Vulnerability (Ref.
125649): Moderate vulnerability (38 of 100).
Nutrients (Ref.
124155): Calcium = 18.3 [10.0, 32.3] mg/100g; Iron = 2.32 [0.96, 5.79] mg/100g; Protein = 24.2 [22.7, 25.5] %; Omega3 = 0.403 [0.246, 0.662] g/100g; Selenium = 42.6 [16.1, 118.0] μg/100g; VitaminA = 21.5 [2.9, 199.3] μg/100g; Zinc = 0.355 [0.211, 0.717] mg/100g (wet weight); based on
nutrient studies.